Angular Lifecycle Hooks
Table of contents
Angular Lifecycle Hooks
Ans1
Angular 12 provides a set of lifecycle hooks that allow you to tap into different phases of a component’s lifecycle and perform custom logic.
The following are the lifecycle hooks available in Angular 12:
- ngOnChanges − This hook is called when one or more of the input properties of a component change. It is used to update the component’s internal state and re-render the view if necessary.
ngOnChanges(changes: SimpleChanges) {
console.log(changes);
}
- ngOnInit − This hook is called after the first ngOnChanges and it is used to initialize the component’s state. This is a good place to make API calls or other initialization logic.
ngOnInit() {
console.log("Component initialized");
}
- ngDoCheck − This hook is called during every change detection cycle and it is used to check for and act on changes that Angular can’t detect on its own.
ngDoCheck() {
console.log("Checking for changes");
}
- ngAfterContentInit −This hook is called after the component’s content has been initialized and projected into the view. It is used to interact with the projected content.
ngAfterContentInit() {
console.log("Content initialized");
}
- ngAfterContentChecked− This hook is called after every change detection cycle that affects the component’s content.
ngAfterContentChecked() {
console.log("Content checked");
}
- ngAfterViewInit − This hook is called after the component’s view and child views have been initialized. It is used to interact with the initialized views.
ngAfterViewInit() {
console.log("View initialized");
}
- ngAfterViewChecked −This hook is called after every change detection cycle that affects the component’s view.
ngAfterViewChecked() {
console.log("View checked");
}
- ngOnDestroy − This hook is called just before a component is destroyed. It is used to clean up any resources or subscriptions that the component has created.
ngOnDestroy() {
console.log("Component destroyed");
}
This hook is called just before Angular destroys the component. You can use it to perform any necessary cleanup operations.
ngOnDestroy() {
this.subscription.unsubscribe();
}
Ans2
Angular creates and renders components along with their children, checks when their data-bound properties change, and destroys them before removing them from the DOM.
Angular offers lifecycle hooks that provide visibility into these key life moments and the ability to act when they occur.
Angular 2 application goes through an entire set of processes or has a lifecycle right from its initiation to the end of the application.
The hooks are executed in this order:
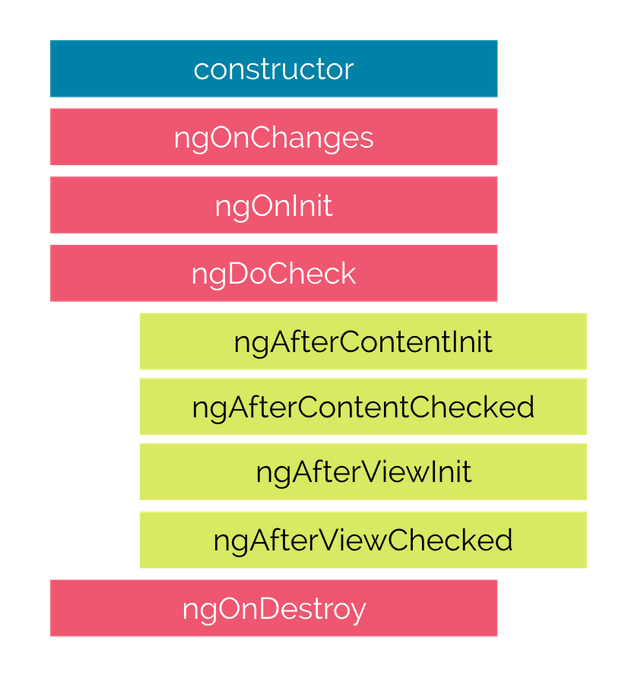
Description of each lifecycle hook.
- ngOnChanges − When the value of a data bound property changes, then this method is called.
- ngOnInit − This is called whenever the initialization of the directive/component after Angular first displays the data-bound properties happens.
- ngDoCheck − This is for the detection and to act on changes that Angular can’t or won’t detect on its own.
- ngAfterContentInit − This is called in response after Angular projects external content into the component’s view.
- ngAfterContentChecked− This is called in response after Angular checks the content projected into the component.
- ngAfterViewInit − This is called in response after Angular initializes the component’s views and child views.
- ngAfterViewChecked − This is called in response after Angular checks the component’s views and child views.
- ngOnDestroy − This is the cleanup phase just before Angular destroys the directive/component.
constructor() vs ngOnInit()
TypeScript classes has a default method called constructor() which is normally used for the initialization purpose. Whereas ngOnInit() method is specific to Angular, especially used to define Angular bindings. Even though constructor() getting called first, it is preferred to use ngOnInit() method for Angular bindings.
Example
export class App implements OnInit{
constructor(){
//called first time before the ngOnInit()
}
ngOnInit(){
//called after the constructor and called after the first ngOnChanges()
}
}